Antibacterial layers | |||
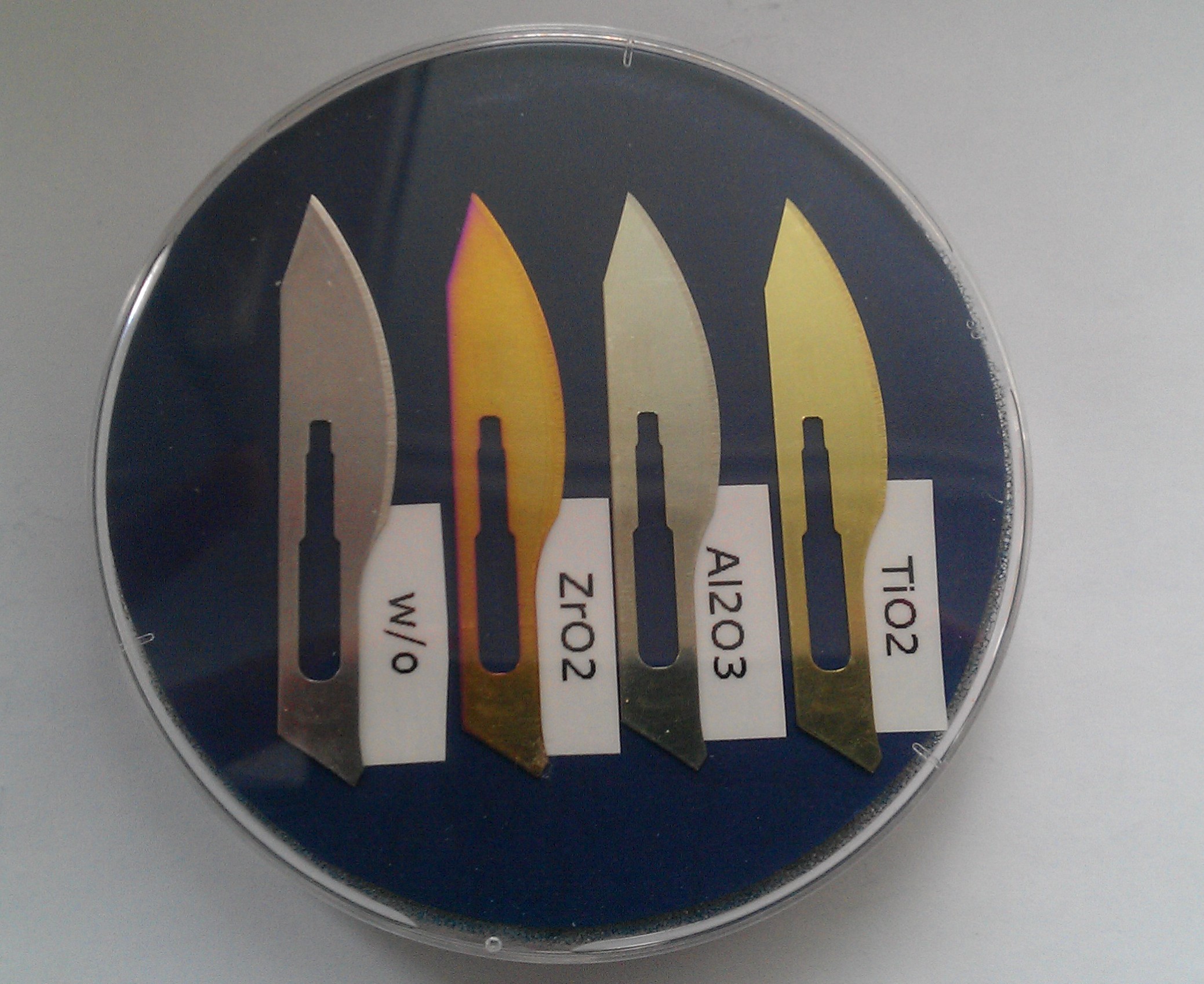
DescriptionWe developed growth method allowing covering of different types of objects, such as surgical instruments, tissues, masks, etc. with the ALD method using oxide thin layers of materials as a antibacterial layer. These layers are deposited at low temperatures (usually below 100°C), which allows for the coating of various substrates, including the soft tissue paper material or surgical instruments, door handles, as well as, synthetic and organic materials.
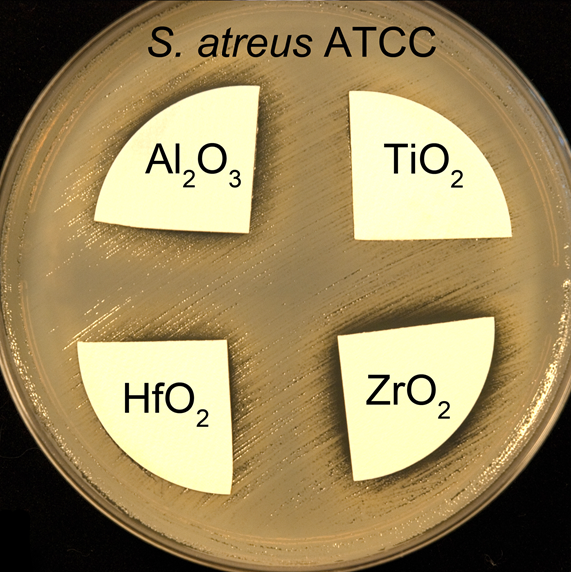
SpecificationIn order to determine the effect of the surface coating with various layers (ZnO, Al2O3, TiO2, HfO2, ZrO2) we tested their antibacterial activity. For this eksperiment we used disk diffusion method, which is normally used to determine drug sensitivity. Paper disks coated with thin oxide layers were tested as Mueller - Hinton agar (BioMórieux) substrates plated with bacterial suspensions in saline solution (0.5 by McFarland). In this studies we tested three bacterial strains:
ApplicationsThe elaborated method of coating on various kinds of surfaces with metal oxides monolayers can be very helpful in reducing the energy and water inputs to processes designed to eliminate micro-organisms (heat sterilization, or chemical), especially in the food industry, production technology and production of animal feed. Potential applications can also be found in medicine, veterinary medicine and the broader health care.
Patent application: P.406853 (15-01-2014)
|
| ||